Demo Objective
In this lesson, we’ll explore the data transformation phase of our ETL process, continuing with our point-of-sale (POS) system scenario. We’ll learn how to clean, format, and prepare the raw transaction data we ingested in the previous lesson, making it ready for analysis and storage.
Note: While we’ll be looking at some code examples in this lesson to understand the concepts, keep in mind that in practice, we’ll be using Apache NiFi. NiFi is a powerful tool with a user-friendly, drag-and-drop for many of these data transformation tasks. The principles we learn here will apply when using NiFi, but the implementation will be more visual and less code-intensive.
Introduction
Welcome to the Data Transformation Phase! This is where we take our raw, ingested data and turn it into something more useful. Data transformation is the process of converting data from its raw form into a cleaner, more structured format that’s ready for analysis or storage.
Transformation Phase
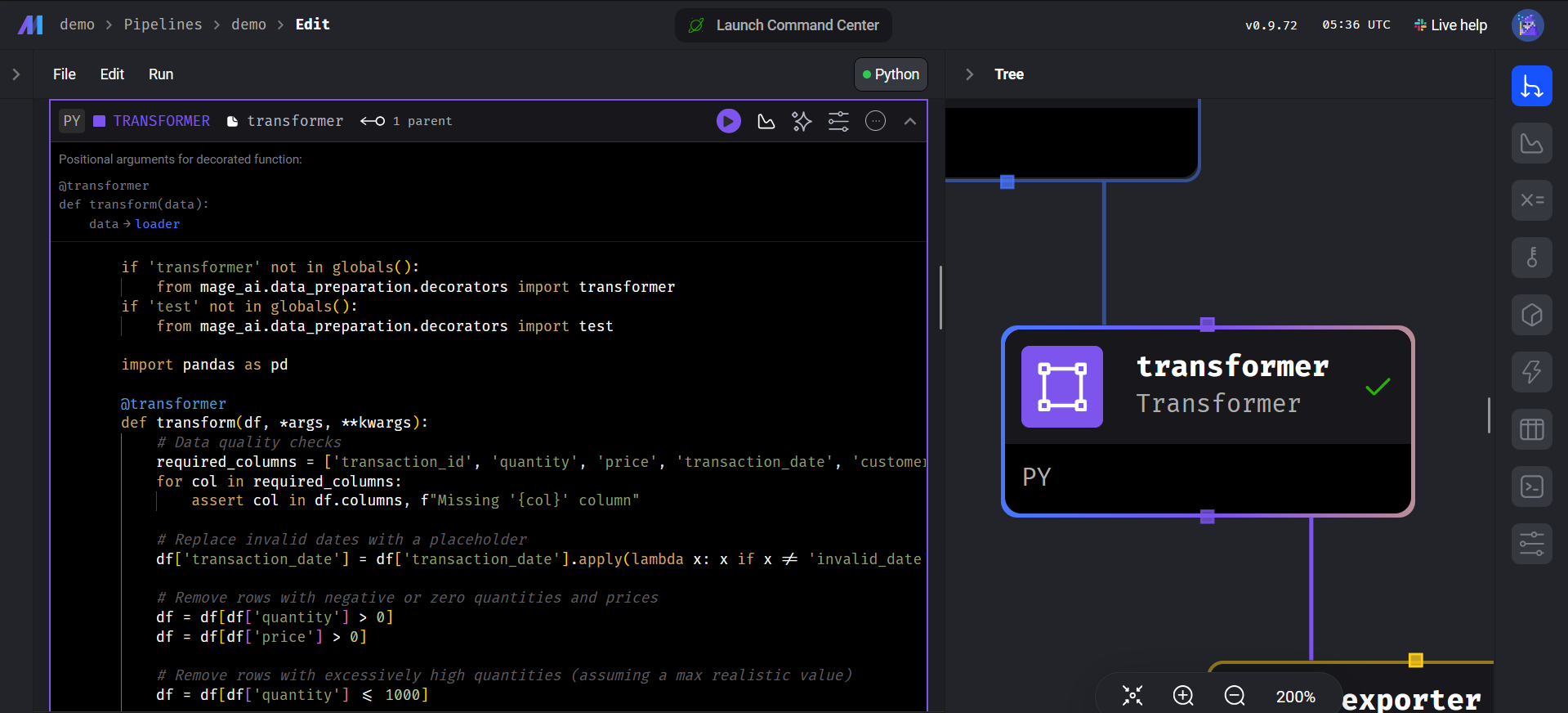
Code Block
Importing Necessary Tools
import pandas as pd
- This line imports the pandas library, which is used for data manipulation and analysis.
Setting Up Special Functions
if 'transformer' not in globals():
from mage_ai.data_preparation.decorators import transformer
if 'test' not in globals():
from mage_ai.data_preparation.decorators import test Data Transformation Function
@transformer
def transform(df, *args, **kwargs):
# ... data cleaning and transformation logic ...
return df
- This function is responsible for cleaning and transforming the data.
- The
@transformerdecorator indicates that this function is part of a data transformation process. - The function takes a DataFrame
dfas input and performs various data cleaning steps.
Data Cleaning Steps
- Checking for required columns: Ensures that essential columns are present in the DataFrame.
- Handling invalid dates: Replaces invalid dates with a placeholder.
- Removing invalid quantities and prices: Eliminates rows with non-positive quantities or prices.
- Handling outliers: Removes rows with excessively high quantities.
- Replacing missing values: Replaces missing values in customer_id, store_id, and product_id with ‘MISSING’.
- Removing duplicates: Removes duplicate transaction IDs.
Testing the Output
@test
def test_output(df) -> None:
# ... assertions to check data quality ...
- This function tests the output of the
transformfunction to ensure data quality. - It checks for:
- The presence of data in the DataFrame.
- All quantities and prices being positive.
- Valid date formats.
- Valid customer ID formats.
Summary
The code defines a function to clean and transform a DataFrame containing transaction data. It performs various checks and transformations to improve data quality. The test_output function verifies that the transformed data meets specific criteria.
In essence, the code is cleaning up messy data to make it ready for analysis.
In the transformation phase, the data underwent specific cleaning and preparation steps, including data type conversions, handling missing values, outlier removal, and data normalization, to ensure data consistency and suitability for subsequent analysis.
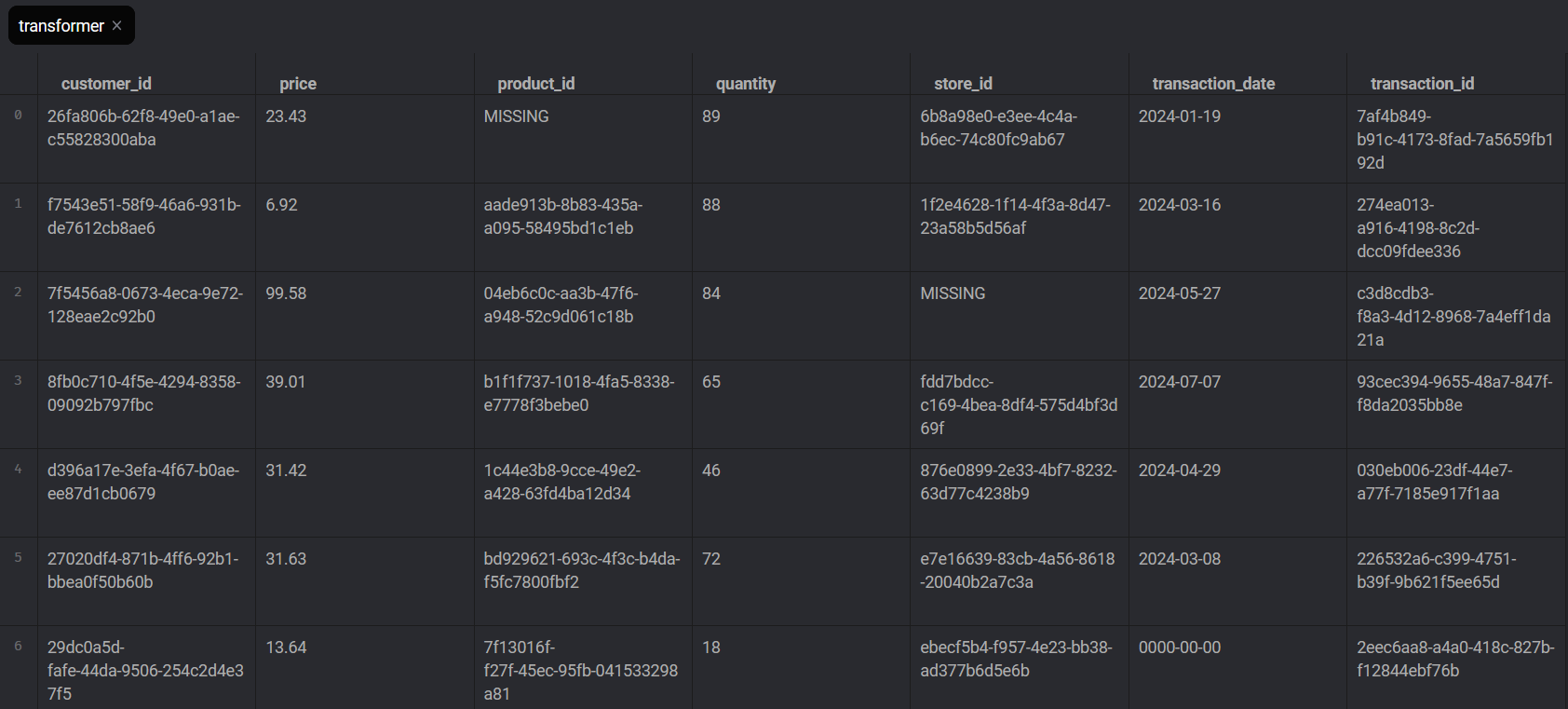
Transform Block Output
Future Learning
As you progress in your data engineering journey, you’ll explore more advanced transformation techniques, including:
- Complex data modeling techniques
- Machine learning for data cleaning and anomaly detection
- Real-time data transformation for streaming data
- Industry-specific transformation rules and best practices
Engagement Activity
Think about data transformation in your daily life. Here are some prompts to get you started:
- When you sort your emails into folders, how is this similar to data transformation?
- If you use a budgeting app, how might it transform your raw spending data into useful categories or summaries?
- How might a news app transform raw news articles into personalized recommendations for you?